What is the reason for sudden breathlessness at night in those with heart disease?
What is the reason for sudden breathlessness at night in those with heart disease?
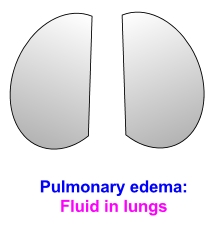
Sudden breathlessness at night in those with known heart disease is usually due to collection of fluid in the lungs (pulmonary edema). During day time, when one is walking about, any extra fluid in the body tends to collect in the legs, due to the effect of gravity. Extra fluid in the body can occur due to failure of heart, kidneys, liver and rarely due to other causes. In heart failure, the extra fluid is due to inability of the heart to pump out blood well. This can occur if the heart muscle is weak or there is obstruction to a valve regulating the flow of blood inside the heart. At night, when one is lying down, extra fluid from the legs gets absorbed into the circulation and gets redistributed into the lungs, which is at a lower position compared to day time (lungs being in the upper part of the body, gets less fluid logged in sitting and standing position). Fluid collection in the lungs makes it heavy and makes breathing more are more difficult. When this reaches a threshold level, the sleeping person wakes up with sudden breathlessness, which gets partially relieved on sitting up for some time, as the lung is no longer in the lowermost part of the body.
Just as water logging occurs in the catchment area of a dam after a heavy rain, fluid collects in the lungs if the valve between the left upper and lower chambers of the heart (mitral valve) is narrowed (mitral stenosis). Similar situation occurs when the left ventricle (lower muscular chamber of the heart) is not able to pump out blood which it receives from the left upper chamber (left atrium). Sudden breathlessness at night is an important symptom which occur in both these conditions. If the breathlessness is not relieved on just sitting up, the person may seek medical help in the emergency department, where medications which increase urine output can clear the lungs. Still higher grades of breathlessness may need non invasive or invasive ventilatory support.