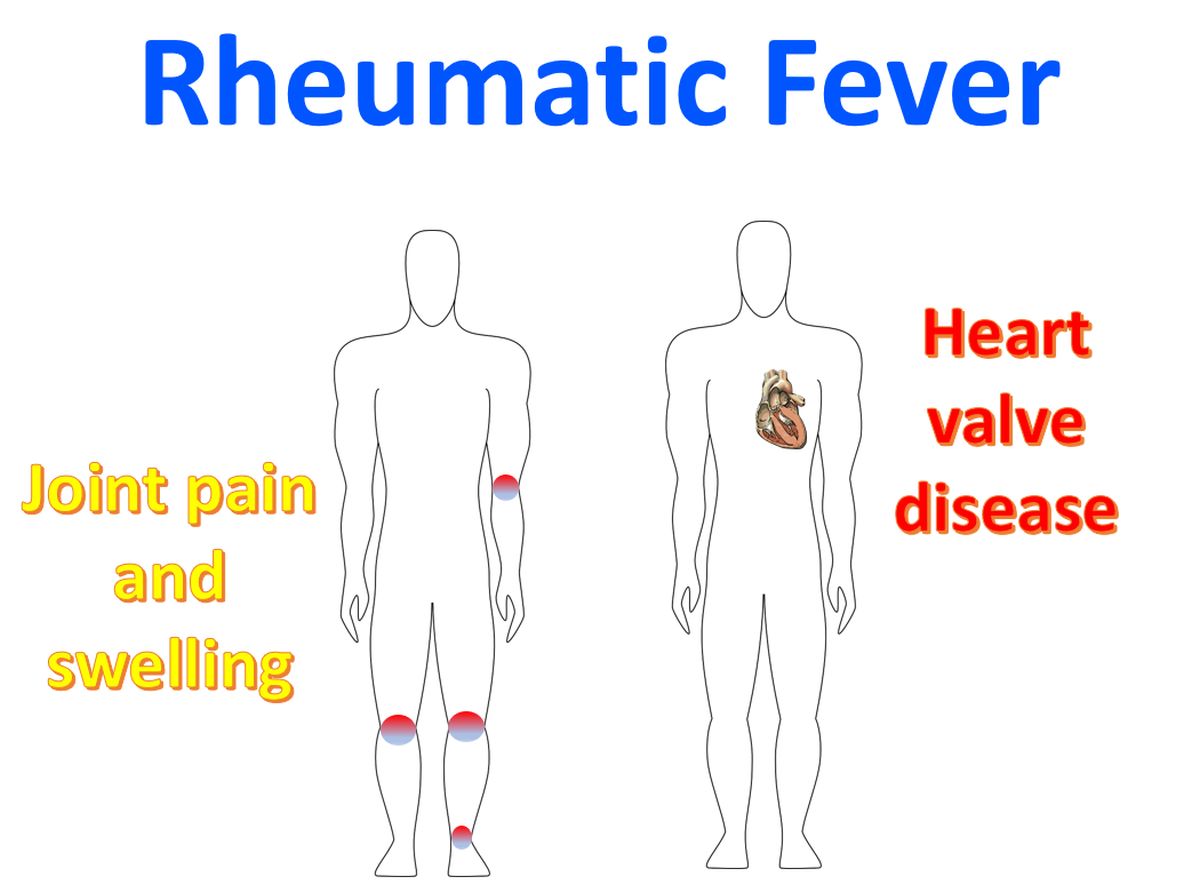
Rheumatic Fever
Rheumatic Fever
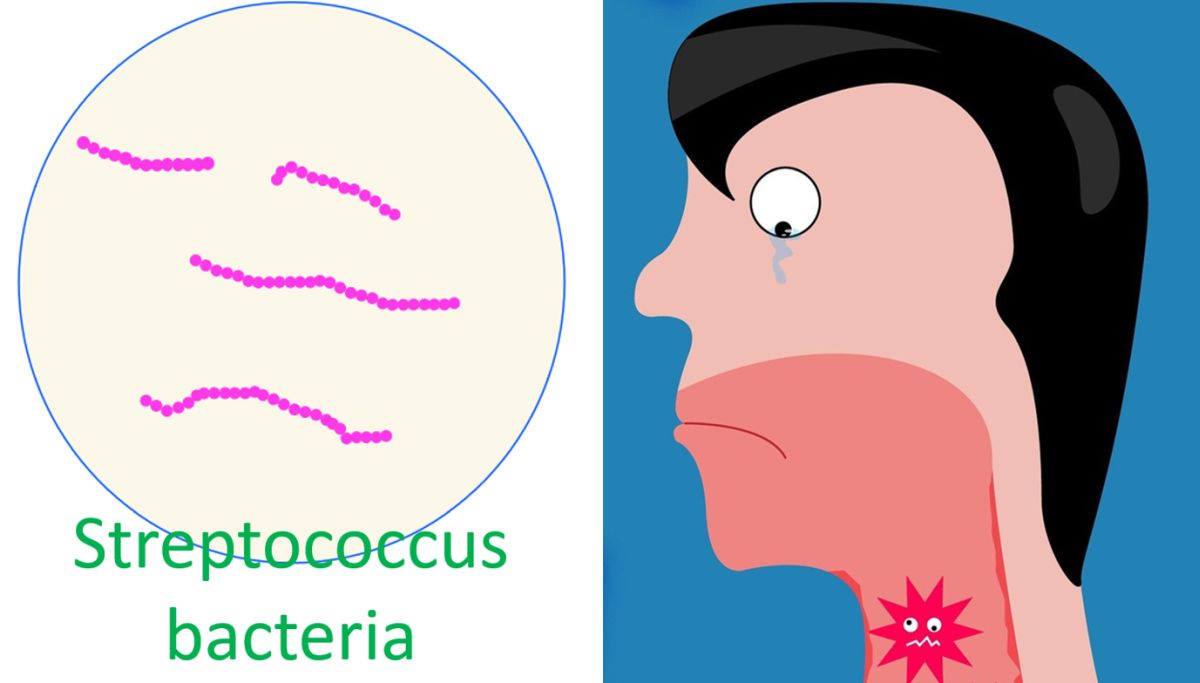
Rheumatic fever is an immune mediated disease involving the joints, heart, skin and brain. Commonest presentation is pain and swelling of multple joints (polyarthritis). Rheumatic fever commonly occurs in childhood and the incidence decreases as age advances. It is extremely uncommon after the age of forty years. Rheumatic fever occurs as a result of cross reaction of antibodies to group A beta hemolytic streptococci with host tissue, most importantly cardiac.
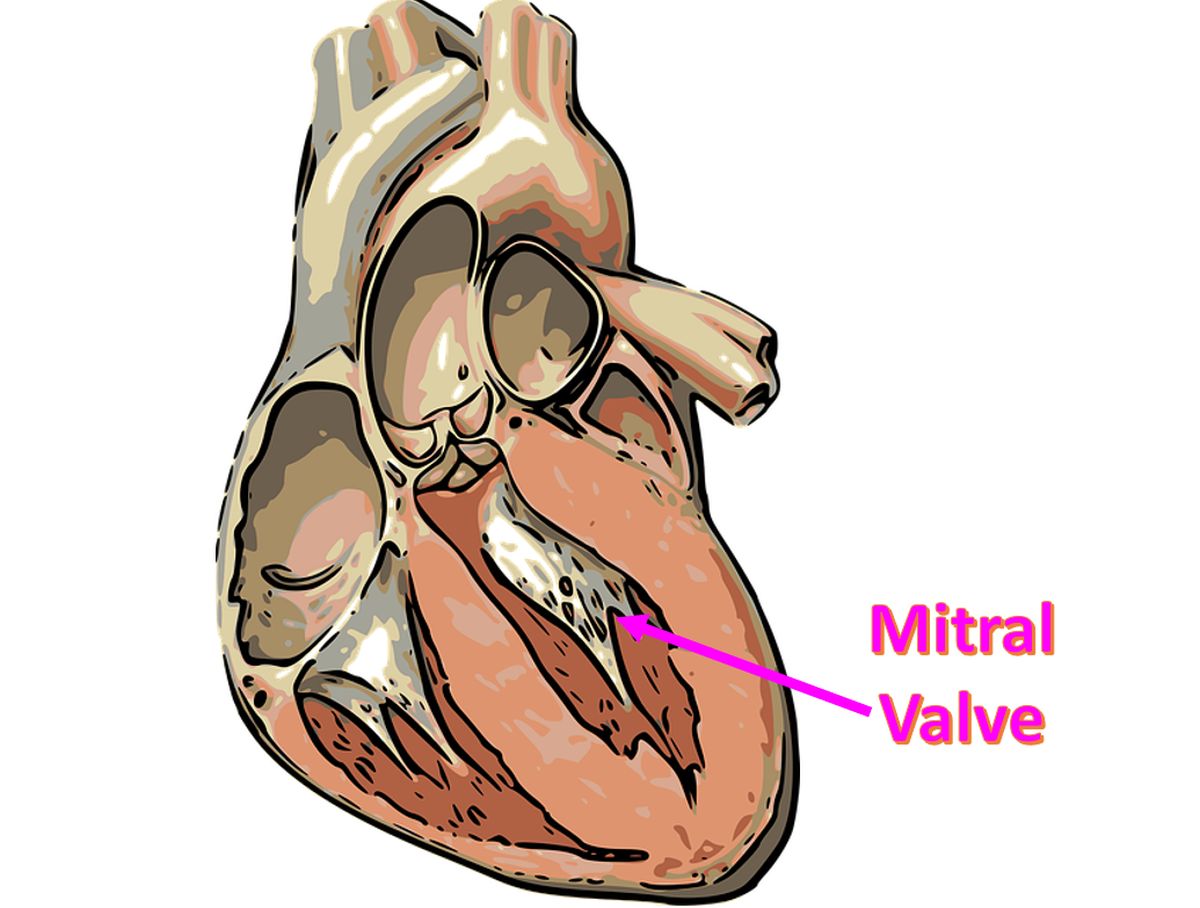
The cardiac manifestation is a pancarditis, involving pericardium, myocardium and endocardium. But the predominant involvment is that of endocardium. The cardiac valves being derived from the endocardium, are the most affected structures. Among the valves, mitral valve is the most commonly involved and aortic, trcuspid and pulmonary valves follow in that order. It is hypothesised that the valve which bears most hemodynamic stress bears the brunt of the damage. Hence mitral valve is most affected as it bears the systolic force of the left ventricle, while the pulmonary valve which bears only the pulmonary diastolic pressure which is very low, suffers least damage.
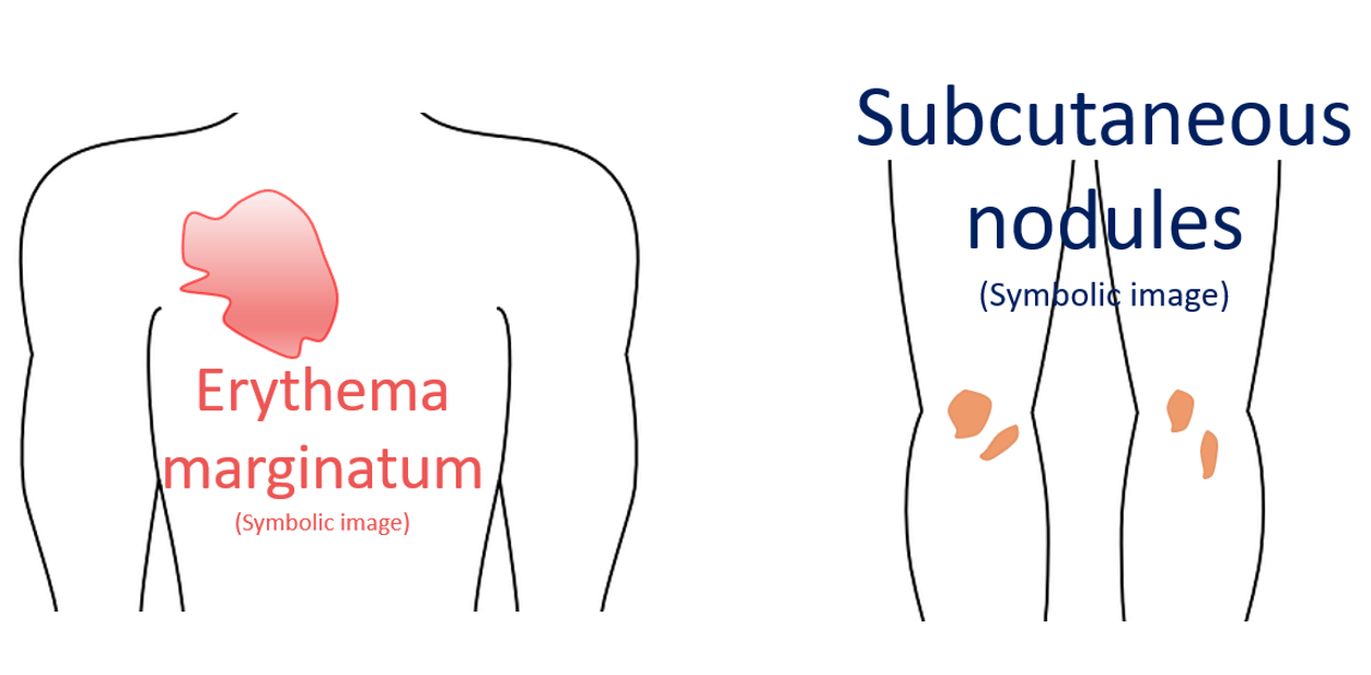
The cardinal manifestations of rheumatic fever are polyarthritis, carditis, chorea, sub cutaneous nodules and erythema marginatum. Polyarthritis is often described as flitting (jumping from one joint to another) and fleeting (transient). Polyarthritis of rheumatic fever usually subsides spontaneously without leaving any sequelae and is non-deforming. Very rarely deformities can occur (Jaccoud’s arthritis). Polyarthritis, carditis, erythema marginatum and subcutaneous nodules are seen in the acute phase while chorea is a late manifestation. Rheumatic chorea is also known as Sydenham’s chorea.
Recurrence of rheumatic fever can be prevented by preventing streptococcal sore throat. This can be achieved by giving long term chemoprophylaxis with long acting penicillin (benzathine penicillin) as monthly injection or oral penicillin on a daily basis. Benzathine penicillin is more effective, possibly because of better compliance. But the higher incidence of anaphylaxis with benzathine penicillin is discouraging clinicians and patients from opting for it.